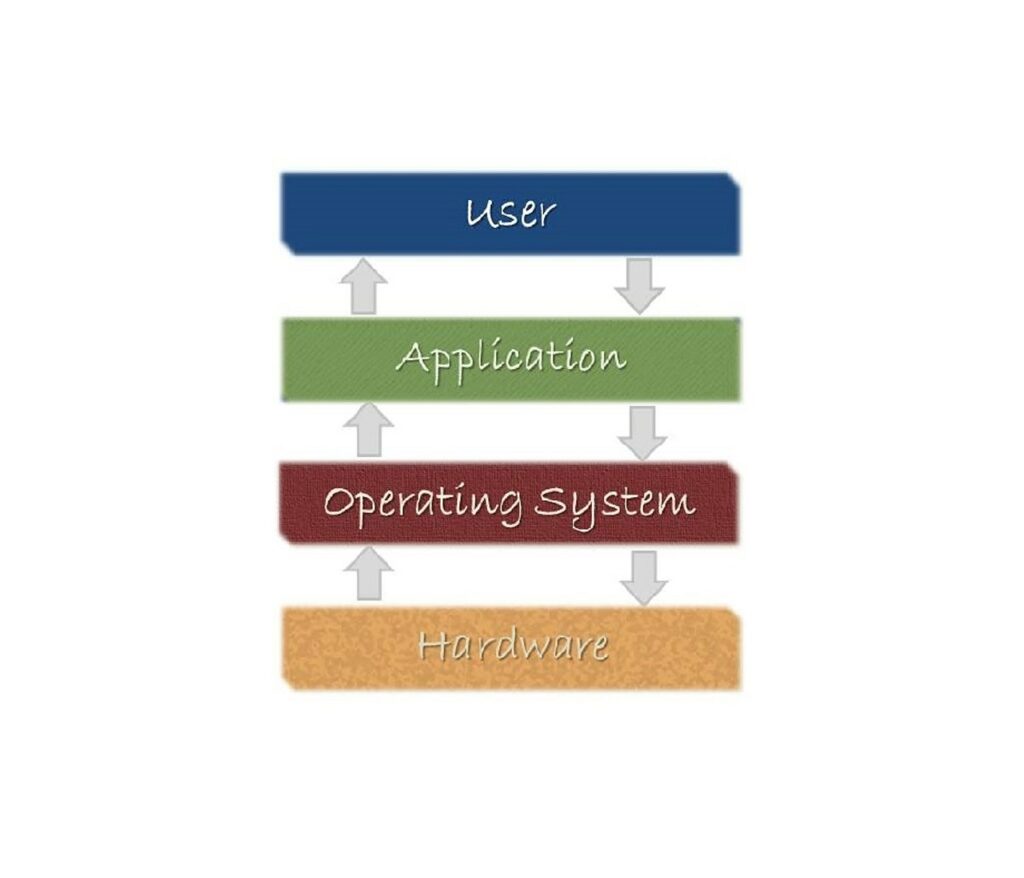
What exactly is an operating system?
An operating system (OS) is a piece of software that serves as a conduit between computer hardware and the user. To execute other applications, every computer system must have at least one operating system. Browsers, MS Office, Notepad Games, and other applications require a certain environment in order to run and fulfill their functions.
The operating system enables you to communicate with a computer without learning its language. A user cannot use a computer or mobile device without first installing an operating system.
The Origins Of OS
- In the late 1950s, operating systems were created to control tape storage.
- In the early 1950s, the General Motors Research Lab built the first operating system for its IBM 701 computer.
- Operating systems began to employ discs in the mid-1960s.
- The original version of the Unix operating system was created in the late 1960s.
- DOS was Microsoft’s initial operating system. It was constructed in 1981 after a Seattle business sold it the 86-DOS software.
- When a GUI was designed and combined with MS-DOS in 1985, the current popular operating system Windows was born.
Various Operating Systems (OS)
The following are the most common OS (Operating System) types:
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
Batch Operating System
Some computer procedures take a long time to complete. A job with comparable demands is batched together and performed as a group to speed up the same process.
A batch operating system’s user never interacts directly with the machine. Every user prepares his or her task on an offline device, such as a punch card, and submits it to the computer operator in this form of OS.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
People at various terminals (shells) can utilize the same computer system at the same time using a time-sharing operating system. Time-sharing refers to the division of processor time (CPU) across many users.
Real-time OS
The time it takes a real-time operating system to process and respond to inputs is extremely short. Military software systems and space software systems are two examples of real-time operating systems.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems make advantage of several processors spread across multiple computers to give extremely rapid computing to their consumers.
Network Operating System
A server runs the Network Operating System. It has the capacity to handle data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking features.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those that are created specifically for smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices.
Android and iOS are two of the most well-known mobile operating systems, while others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.